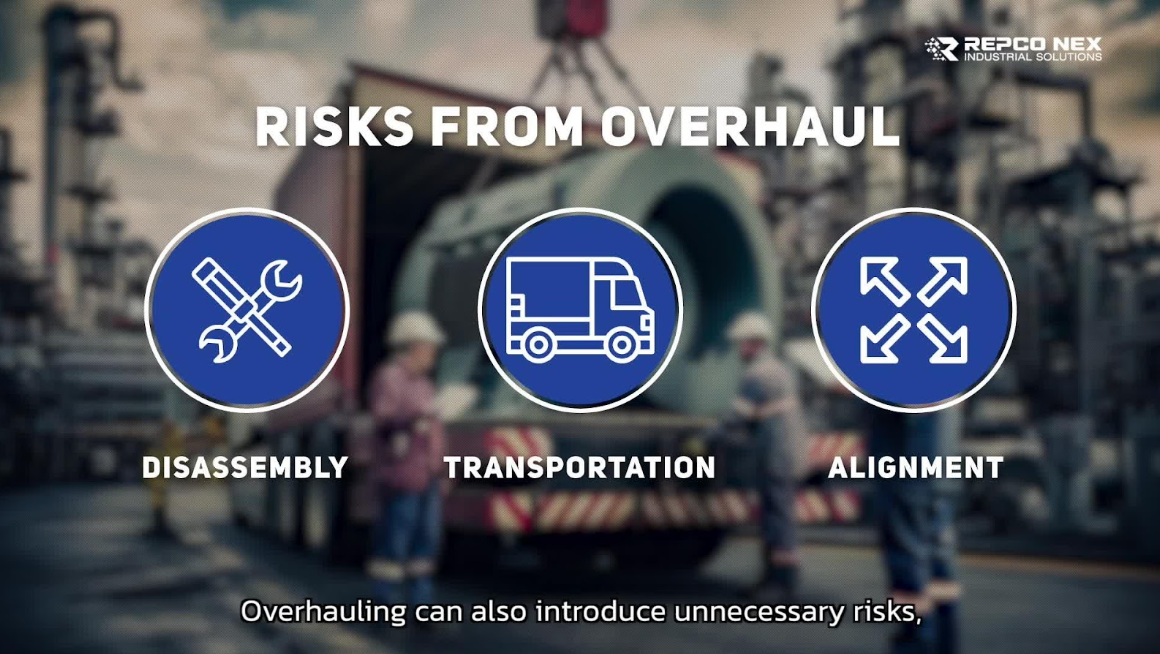
Motors are at the heart of every industrial plant.
From the statistical data, it was found that motor damage can occur in many forms, including:
1. Damage to the bearing accounted for approximately 41%, with problems encountered due to lack of lubricants. normal aging or installation errors
2. Damage caused to the winding (winding) accounted for approximately 37%, with problems encountered from the shortening of the windings in the motor. This can be caused by a malfunction within the winding (short turn), contamination of grease entering the motor, or moisture inside the motor.
3. Rotor damage accounted for approximately 10%, with problems found in rotor bar or end ring damage due to thermal fatigue for frequent cyclic motors.
4. Other damage accounted for approximately 12%, with problems such as loose wire connectors, corrosion in the mounting or casing, as well as some winding insulation defects in high-voltage motors (partial discharge).
The damage of the motor can be caused by many reasons as mentioned above. Typical machine health checks by insulation resistance test or vibration analysis may not be able to detect complete and timely malfunctions. causing the motor to be damaged before without us knowing in advance causing production to stop.